How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone piloting, covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. We’ll delve into the intricacies of drone controls, camera operation, and maintenance, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
Understanding the fundamentals of drone operation is crucial for both safety and successful flights. This guide will equip you with the necessary knowledge and techniques to navigate various flight scenarios, capture stunning visuals, and maintain your drone for optimal performance. We’ll explore the technical aspects, including understanding different flight modes and camera settings, while also addressing the legal and ethical implications of drone usage.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone

Before you even think about taking off, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for a safe and successful drone flight. This involves inspecting key components, verifying system functionality, and planning for potential emergencies. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents and equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures your drone is in optimal condition. This includes checking the battery level (ensuring it’s sufficiently charged and not showing signs of damage), visually inspecting propellers for cracks or damage, and verifying a strong GPS signal for accurate positioning and flight stability. Checking the gimbal and camera for proper functionality is also vital for capturing quality footage.
Pre-Flight Safety Check
This detailed checklist helps mitigate risks and ensures a smooth flight. The steps involve systematically examining each component, documenting the findings, and taking appropriate action if necessary. Remember to always prioritize safety.
| Item | Check | Notes | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Sufficient charge? | Check voltage and remaining flight time. | Replace if below minimum threshold. |
| Propellers | Intact and securely attached? | Look for cracks, bends, or damage. | Replace damaged propellers. |
| GPS Signal | Strong signal? Sufficient satellites acquired? | Check the GPS indicator on your controller. | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception if necessary. |
| Gimbal and Camera | Functioning correctly? | Test camera operation and gimbal movement. | Troubleshoot any issues before flight. |
| Flight Environment | Safe and legal airspace? Obstacles identified? | Check for obstructions, weather conditions, and airspace restrictions. | Adjust flight plan or postpone flight if necessary. |
Emergency Procedures
Knowing what to do in an emergency is paramount. Loss of signal is a common concern, often triggered by distance or interference. In such cases, the drone’s Return-to-Home (RTH) function should automatically engage, bringing the drone back to its starting point. However, always be prepared to manually take control if necessary. Unexpected malfunctions require a calm and decisive response; prioritize safe landing procedures, and always consider the safety of people and property.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective operation. Understanding the basic flight commands and different flight modes will allow you to navigate with precision and confidence.
Basic Drone Controls
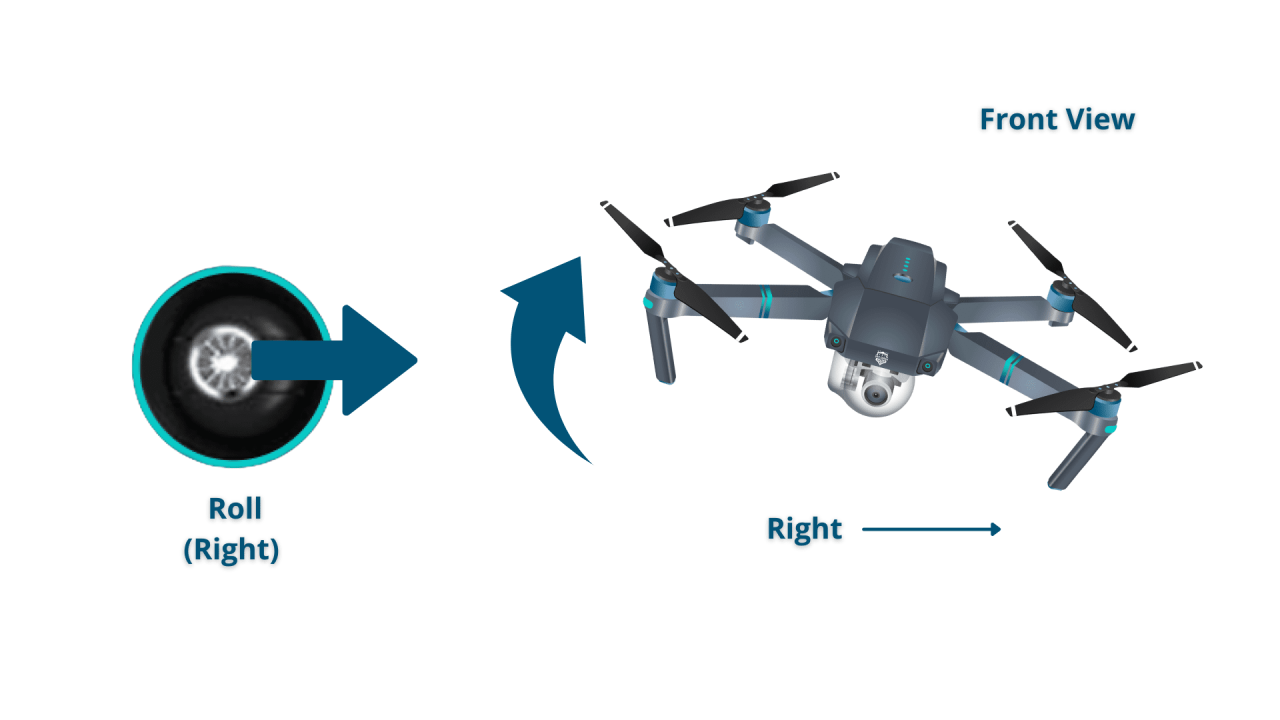
Most drones use a control system based on four primary axes: throttle (controls altitude), yaw (rotates the drone left or right), pitch (tilts the drone forward or backward), and roll (tilts the drone left or right). These controls work in conjunction to maneuver the drone in three-dimensional space.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, aiding in smooth control. Sport mode increases speed and responsiveness, ideal for experienced pilots. GPS mode utilizes satellite data for precise positioning and stability, assisting with autonomous functions.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. Learning the fundamentals is crucial before tackling more advanced techniques, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This site provides valuable insights into safe and effective drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks to emergency procedures. Ultimately, consistent practice and a good understanding of the regulations are key to becoming a proficient drone pilot.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
- Ensure pre-flight checks are complete.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS (if necessary).
- Slowly increase the throttle to lift off vertically.
- Use subtle adjustments to maintain a stable hover.
- To land, gently lower the throttle until the drone touches down smoothly.
Drone Navigation Using Waypoints
Waypoints allow for pre-planned flight paths. Most drone software allows you to set a series of waypoints on a map, creating a route the drone will follow autonomously. This is particularly useful for aerial photography or videography where consistent and precise movements are required.
Mastering Drone Camera Operation
The camera is a key feature of most drones. Understanding its settings and capabilities is essential for capturing high-quality images and videos.
Camera Settings and Their Effects
Camera settings like ISO (light sensitivity), shutter speed (exposure time), and aperture (amount of light entering the lens) significantly impact image quality. Higher ISO values are suitable for low-light conditions but can introduce noise. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion but require more light, while slower speeds blur motion but work well in low light. Aperture controls depth of field, with wider apertures creating shallow depth of field (blurred background) and narrower apertures creating greater depth of field (sharp foreground and background).
Adjusting Camera Angle and Gimbal Settings
The gimbal allows for smooth and stable camera movements. Adjusting the gimbal’s tilt, pan, and roll allows for precise framing and shot composition. Experiment with different angles to achieve the desired perspective.
Recording High-Quality Video Footage
For high-quality video, maintain a steady flight, use appropriate camera settings (as discussed above), and ensure sufficient lighting. Smooth movements and consistent framing are crucial for professional-looking footage.
Simple Video Shoot Plan, How to operate a drone
A basic plan might include establishing shots (wide shots of the location), detail shots (close-ups of interesting features), and tracking shots (following a moving subject). Varying shot types adds visual interest and dynamism to your video.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers and Techniques
Advanced techniques enhance your drone piloting skills and allow for creative aerial shots. These require practice and a thorough understanding of drone controls.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible and proficient drone piloting requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of regulations.
Flight Techniques
Smooth transitions between shots involve precise control of the drone’s movements to avoid jerky or abrupt changes in perspective. Precise hovering requires mastering the throttle and other controls to maintain a stable position in the air.
Common Piloting Errors
Common errors include losing orientation, exceeding the drone’s limits (range, battery life), and failing to account for wind conditions. Careful planning and awareness of environmental factors minimize these risks.
Advanced Features
Obstacle avoidance systems automatically detect and avoid obstacles, enhancing safety. Return-to-home (RTH) functionality brings the drone back to its starting point automatically in case of signal loss or low battery.
Performing a 360-Degree Aerial Shot

- Find a suitable location with ample space.
- Position the drone at the desired altitude and distance from the subject.
- Use the yaw control to smoothly rotate the drone 360 degrees around the subject.
- Maintain a steady altitude and distance throughout the maneuver.
- Ensure smooth and consistent camera movements.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage significantly extend the lifespan of your drone. Following these guidelines will keep your drone in optimal condition.
Cleaning and Maintaining Drone Components
Regularly clean the drone body, propellers, and camera lens with a soft cloth. Inspect for any signs of damage or wear and tear. Lubricate moving parts as needed according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Safe Storage Environment
Store your drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Keep it in a protective case to prevent damage during transportation and storage.
Maintenance Schedule
- Daily: Inspect propellers and body for damage.
- Weekly: Clean the drone and camera lens.
- Monthly: Check battery health and calibrate the compass.
- Quarterly: Perform a thorough inspection of all components.
Proper Battery Storage and Charging
Store batteries in a cool, dry place at around 50% charge to prolong their lifespan. Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow charging instructions carefully.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to legal regulations and ethical guidelines. This ensures safe and respectful drone operation.
Legal Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Many countries have regulations governing drone operation, including airspace restrictions near airports and other sensitive areas. It’s crucial to research and understand these regulations before flying.
Responsible Drone Piloting
Responsible drone piloting involves respecting others’ privacy, avoiding hazardous situations (such as flying near people or buildings), and following all applicable regulations. Always be mindful of your surroundings and fly safely.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
In some locations, permits or licenses may be required to operate a drone, especially for commercial use or in specific airspace. Always check local regulations and obtain the necessary authorizations before flying.
Drone Regulations Overview
| Regulation | Description | Location | Penalties for Violation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Flight Altitude | Restriction on how high you can fly. | Varies by location and airspace. | Fines, license suspension, or legal action. |
| No-Fly Zones | Areas where drone operation is prohibited. | Near airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas. | Fines, license suspension, or legal action. |
| Registration Requirements | Requirement to register your drone with authorities. | Varies by country and region. | Fines or legal action. |
| Privacy Laws | Regulations concerning the collection and use of images and data. | Varies by jurisdiction. | Fines, legal action, or civil lawsuits. |
Mastering drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and practice. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, and consistently prioritizing safety and responsible piloting, you will be well-equipped to explore the exciting world of aerial technology. Remember to always check local regulations and prioritize safe flight practices above all else. With dedication and practice, you’ll soon be capturing stunning aerial footage and experiencing the thrill of flight from a unique perspective.
Query Resolution
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and beginner modes are ideal for starting. Look for features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How long does a drone battery last?
Flight time varies depending on the drone model and conditions, typically ranging from 15 to 30 minutes per battery.
What is the legal age to fly a drone?
Legal age varies by country and region. Check local regulations for specific requirements.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If this fails, attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, report the loss to relevant authorities.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is recommended before each flight, especially if the drone has been moved significantly.